News
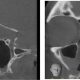

Understanding Dental CBCT and Its Role in Maxillary Sinus Evaluation
July 22, 2024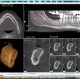

Exploring the Features of ICAT CBCT Software: A Comprehensive Overview
October 14, 2024Exploring the Precision of Dental CT scans in Diagnosis and Reporting
In the realm of dentistry, precision is paramount. From diagnosing complex oral conditions to planning intricate surgical procedures, the ability to visualise structures in high detail can make all the difference. This is where CBCT scans steps in as a revolutionary tool, offering dentists a three-dimensional view of the oral and maxillofacial region with unparalleled clarity. In this blog, we delve into how the dental CT scan is utilised to report and diagnose various dental conditions.
Understanding Dental CBCT Scans
Cone Beam Computed Tomography, commonly referred to as CBCT, is a specialised type of medical imaging technique used primarily in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. Unlike traditional two-dimensional dental imaging, which provide a flat image of the teeth and surrounding structures, CBCT scans generate a three-dimensional image of the entire oral and maxillofacial region.
CBCT scanners operate by rotating around the patient's head, capturing multiple x-ray images from different angles. These images are then reconstructed into a three-dimensional model using advanced computer algorithms. The result is a detailed, high-resolution image that allows dental professionals to visualise teeth, bones, nerves, soft tissues, and other anatomical structures with exceptional clarity.
Applications in Diagnosis
1. Endodontics
Dental CT scans play a crucial role in endodontic diagnosis by providing detailed images of the root canal system. Dentists can accurately assess the complexity of root canal anatomy, detect the presence of infections, and identify any abnormalities such as calcifications or root fractures. This information is invaluable for planning and executing successful root canal treatments.
2. Implant Planning
CBCT scans are indispensable in dental implantology for precisely planning the placement of dental implants. By visualising the bone structure in three dimensions, dentists can identify the optimal locations for implant placement, assess bone density and quality, and avoid vital structures such as nerves and sinuses. This results in more predictable outcomes and reduces the risk of complications during implant surgery.
3. Orthodontics
In orthodontic treatment planning, dental CT scans provide detailed information about the position, orientation, and morphology of teeth and surrounding bone. Orthodontists can accurately assess skeletal relationships, identify impacted teeth, evaluate airway dimensions, and anticipate potential challenges before initiating treatment. This comprehensive understanding allows for more precise treatment planning and better outcomes for patients.
4. TMJ Disorders
CBCT scans are instrumental in diagnosing temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders by visualising the bony structures of the temporomandibular joint in three dimensions. Dentists can assess condylar morphology, evaluate joint space, detect osteoarthritis, and identify any structural abnormalities contributing to TMJ dysfunction. This information guides treatment decisions and helps in developing personalised treatment plans for patients with TMJ disorders.
Reporting and Interpretation
Interpreting dental CT scans requires specialised training and expertise due to the complexity of three-dimensional anatomy. Dental professionals, typically oral and maxillofacial radiologists, or experienced dentists, carefully analyse CBCT scan images to provide accurate reports and diagnoses. These reports detail findings such as the presence of pathology, anatomical variations, dental anomalies, and other relevant information essential for treatment planning.
CBCT reports may include:
- Description of anatomical structures and landmarks. - Identification of pathology, such as cysts, tumors, or infections. - Assessment of bone quality, density, and volume. - Evaluation of dental and skeletal relationships. - Recommendations for treatment or further diagnostic procedures.
Conclusion
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) has revolutionised the field of dentistry by providing detailed three-dimensional images of the oral and maxillofacial region. From diagnosis to treatment planning, CBCT scans offer unparalleled precision, allowing dental professionals to make informed decisions and deliver optimal care to their patients. By leveraging the power of advanced imaging technology, dentists can achieve superior clinical outcomes while ensuring patient safety and comfort.
To be able to report on your Dental CT scans you must complete the mandatory Level Two (Further) Training in Dental CBCT Justification and Interpretation course. Copy the link into your browser to take you to the course page.
https://education.cavendishimaging.com/course/107/Level-2-Further-training-in-dental-CBCT-justification-and-image-interpretation/
We have also launched our new ‘Reporting with Confidence’ programme, a 6-week radiologist-led reporting programme which is designed for clinicians who are not feeling comfortable reporting their own CBCT scans. Copy the link into your browser to take you to the course page.
https://education.cavendishimaging.com/course/1154/Reporting-With-Confidence-After-Level-Two---Kick-Off/


